File Permissions in Linux
Project Description
In this lab, I demonstrated the use of Linux commands to configure file authorization. Authorization is essential for granting access to specific system resources, ensuring that unauthorized users cannot access or modify sensitive files, which is critical for system security. In Linux, file and directory permissions are used to define who can access particular files and directories.
As a security analyst, setting appropriate access permissions is crucial to protecting sensitive information and maintaining overall system security.
Steps to Check File and Directory Details
In this scenario, I examined and managed file permissions in the /home/researcher2/projects directory
for the user researcher2, who is part of the research_team group.
By using the command ls -la, I verified the permissions for all files in the directory,
including hidden files, to ensure they aligned with proper authorization practices.
- First, I confirmed the current directory using
pwdcommand then listed all directories with thelscommand. - Next, I accessed the projects directory (
cd projects) and checked the permissions for all files, including hidden ones, usingls -la.
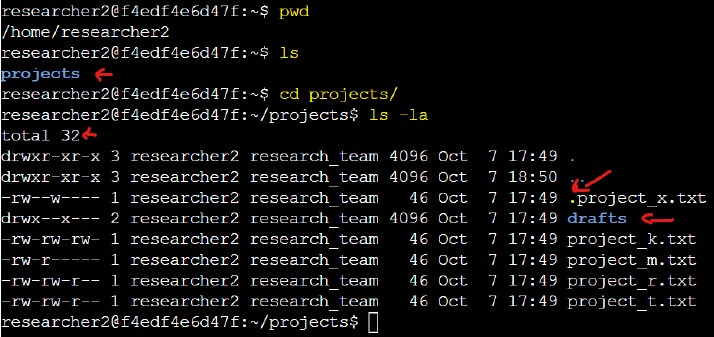
A dot (.) preceding a file or directory name indicates a hidden item. For instance, in this folder,
the file .project_x.txt is hidden.
Understanding the Permissions String
Each file or directory entry starts with a drwxrwxrwx represents a directory where the owner, group,
and others have full permissions:
- The 1st character indicates the file type (
dfor directory,-for a regular file). - The 2nd-4th characters represent the user's permissions (read
r, writew, executex). - The 5th-7th characters indicate the group's permissions.
- The 8th-10th characters represent permissions for others.
Changing File Permissions
In this task, I determined whether any files had incorrect permissions and modified them as necessary. This action removed unauthorized access and enhanced the security of the system.
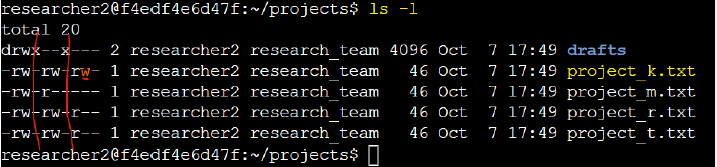
>> None of the files should allow other users to write to them.
To check the current permissions, I used the ls -l command.
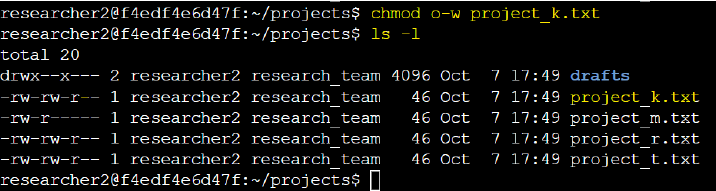
To remove write (w) permission for "others" (o), I executed the chmod command:
chmod o-w project_k.txt, where o refers to others (the last 3 characters in the string), and -
removes the write permission.
Changing File Permissions on a Hidden File
The file .project_x.txt is a hidden file that has been archived and should not be written to by
anyone. The user and group should still be able to read this file. To check the hidden file's permissions, I ran the
ls -la command.
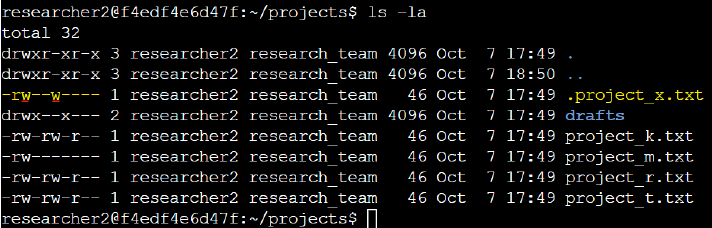
I observed that the hidden file .project_x.txt had write (w) permission for the user (1st instance) and
the group (2nd instance). To enforce read-only access, I removed the write permissions with the command:
chmod u-w,g-w,g+r .project_x.txt.
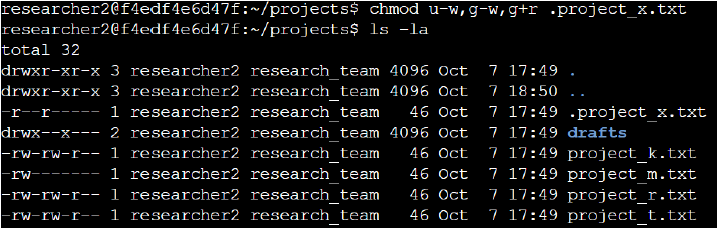
Modifying Directory Permissions
I also reviewed the permissions of the /home/researcher2/projects/drafts directory.
>> Only the researcher2 user should have access.
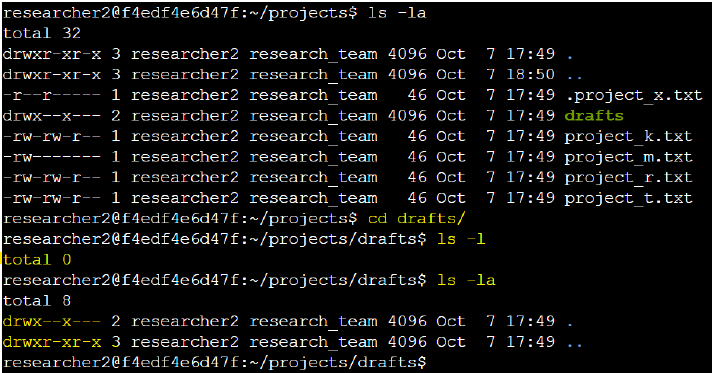
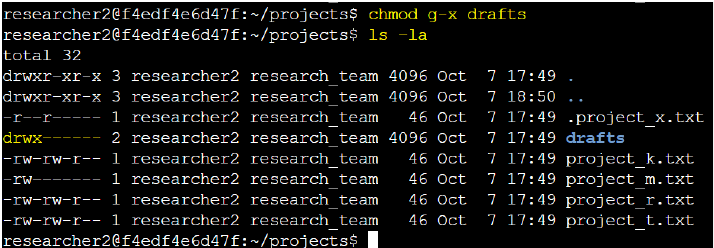
To ensure this, I adjusted the permissions to allow only execute (x) privileges for the user with the command:
chmod g-x drafts.
Summary
In this lab, I practiced fundamental Linux commands to:
- Examine file and directory permissions,
- Change file permissions, and
- Secure directory permissions.
These exercises reinforced key concepts in securing Linux systems by managing access to sensitive resources.