Applying Filters to SQL Queries
Project Description
In this lab, I worked on various SQL queries to apply filters to login and employee data based on specific conditions. The objective was to retrieve data for different scenarios, such as identifying failed login attempts outside business hours, locating employees in specific departments, and excluding records based on department or location. These queries leveraged SQL operators such as AND, OR, NOT, and LIKE to filter data efficiently and ensure system security.
Task 1 - Retrieve After-Hours Failed Login Attempts
In this task, I investigated failed login attempts made after business hours by querying the login activity data. The success column, which contains boolean values (stored as 1 for TRUE and 0 for FALSE in MySQL), was used to identify whether the login attempts were successful or not.
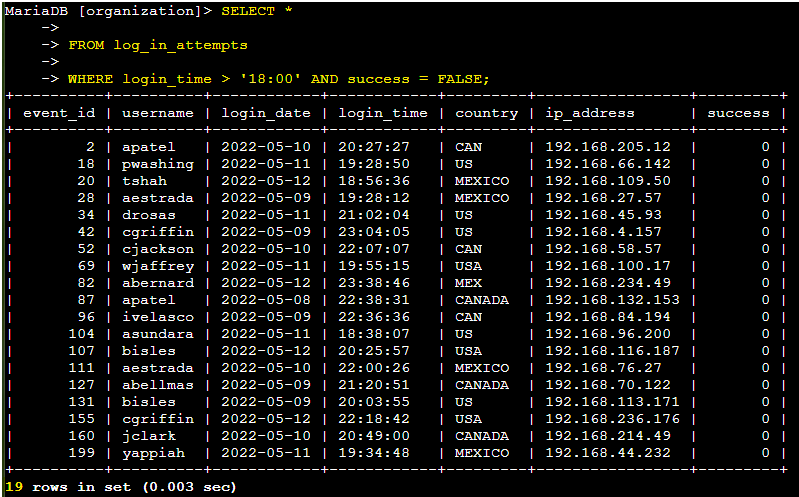
The query filtered for failed login attempts that took place after 18:00. I began by selecting all data from the log_in_attempts table. Then, I applied a WHERE clause combined with an AND operator to refine my results, ensuring that only unsuccessful login attempts after 18:00 were included. The first condition, login_time > '18:00', filters for attempts made after that time, while the second condition, success = FALSE, targets the failed login attempts.
Task 2 - Retrieve Login Attempts on Specific Dates
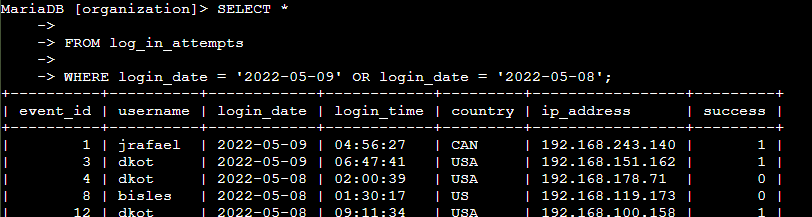
I investigated a suspicious event that occurred on '2022-05-09'. The objective was to retrieve all login attempts that took place on that day and the day before, '2022-05-08'. The login_date column in the log_in_attempts table was utilized to obtain the dates when login attempts were made.
Using the OR operator, I filtered the data to retrieve failed login attempts that occurred on either of the specified dates. This query was designed to assist in tracking login activities around the time of the suspicious event and help identify potential unauthorized access or unusual behavior.
SELECT * FROM log_in_attempts WHERE login_date = '2022-05-09' OR login_date = '2022-05-08';
Task 3 - Retrieve Login Attempts Outside Specific Country
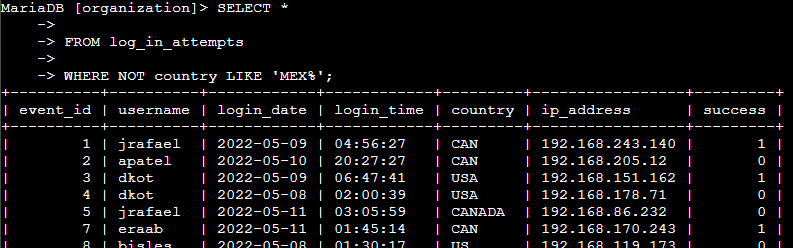
I investigated login attempts that did not originate in Mexico. The goal was to identify login attempts where the country field was not listed as 'MEX' or 'MEXICO'. The country field contained entries that either started with 'MEX' or were fully written as 'MEXICO'. To retrieve login attempts from other countries, I used the NOT and LIKE operators with the matching pattern 'MEX%'.
SELECT * FROM log_in_attempts WHERE NOT country LIKE 'MEX%';
Task 4 - Retrieve Employees in Specific Department
For this task, I consulted another table (employees) as the information I wanted (department and office columns) was in it. To first view and better understand the employees table, I selected all columns from this table.
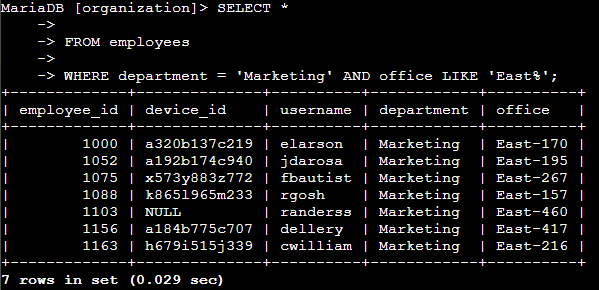
I retrieved information about employees in the 'Marketing' department who are located in the East building, such as in offices labeled 'East-170' or 'East-320'. The employees table was queried, selecting all columns to gather the necessary information. I applied filters on the department column to limit the results to the 'Marketing' department, and the office column was filtered using the pattern 'East%' to capture all relevant offices within the East building.
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE department = 'Marketing' AND office LIKE 'East%';
Task 5 - Retrieve Employees in Distinct Departments
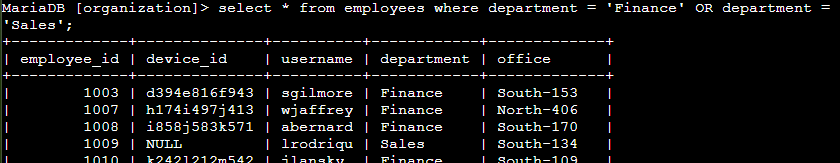
I assisted in locating information on employees in the 'Finance' and 'Sales' departments to facilitate a computer update. Using the employees table, I wrote an SQL query to retrieve records for employees belonging to either the 'Finance' or 'Sales' department. The query used the OR operator to filter records based on the department column, ensuring that employees from both departments were included.
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE department = 'Finance' OR department = 'Sales';
Task 6 - Retrieve All Employees Not in IT
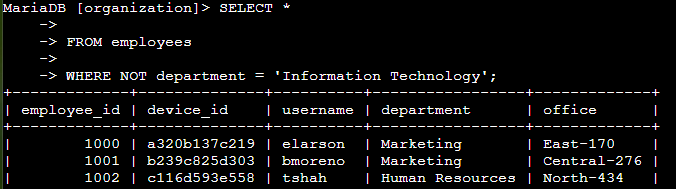
Finally, I located employee information for those not in the 'Information Technology' department, as their computers still needed an update. Using the employees table, I wrote an SQL query to retrieve records for employees who were not part of the 'Information Technology' department. By applying the NOT operator to the department column, I filtered out employees from IT.
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE NOT department = 'Information Technology';
Summary
Throughout this lab, I demonstrated the use of SQL queries to address real-world scenarios by filtering data based on dates, times, patterns, and multiple conditions. I used the LIKE operator to search for patterns in office locations, and applied filters on date and time to retrieve login activities after hours. Additionally, I used AND, OR, and NOT to filter data based on department or country information, ensuring precise results for each scenario. These tasks highlighted my ability to extract meaningful data from large datasets, supporting security and IT operations.